Liquidity ratio analysis can be defined as the measurement of the short-term solvency of a company. Although examining organizations’ profitability and efficiency is crucial, liquidity risks remain very real and serious, as demonstrated by the 9/11, Lehman, and COVID crises. We then divide the quick assets by the average daily cash expense to obtain the number of days those quick assets can cover. The higher this liquidity ratio, the more comfortably a company can face adverse liquidity events. It means that this company collected its accounts receivable 2-times faster than it sold credit and had an average AR balance of just one-fifth of its annual credit sales.
Define operating liquidity
In addition to cash and account balances, this also includes securities that can be sold quickly, such as shares, and investments with short maturities, such as treasury bills. Accounts receivable and inventories are also included in liquidity under certain circumstances. Key solvency ratios are the debt-to-equity Ratio and interest coverage ratio. A high debt-to-equity ratio indicates the brokerage has a risky amount of debt relative to its equity capital. The interest coverage ratio measures how easily a brokerage service receives its interest costs from operating income.
Company360 plans
- So, while liquidity is certainly important, investors should keep the bigger picture in mind rather than assuming that a higher liquidity ratio is inherently better.
- A higher debt-to-equity ratio indicates that more of the company’s assets are funded by creditors than shareholders, which can be risky.
- It is the result of subtracting the Current Liabilities from the Current Assets.
Considering the liquid assets, present financial obligations are analysed to validate the safety limit of a company. Apart from all the above stated liquid ratios, Basic Liquid Ratio is not based on the company’s financial status. But it’s an individual financial ratio which indicates a schedule for how far a family can finance its requirement with its liquid assets.
Understanding AI in Finance and Its Impact on Businesses
Remembering that all numbers are in thousands, this means their Current Assets exceed their Current Liabilities by more than $151 million dollars. For their size, Sprouts has plenty of Net Working Capital and is in no danger defaulting on its short-term obligations. Thanks to our well-designed and well-thought-out templates, you can now anticipate that your work will become simpler. A template can be used for multiple actions, including invoices, quotes, purchase orders, back orders, bills, and payment receipts. An online accounting and invoicing application, Deskera Books is designed to make your life easier.

Measurement of liquidity
An analysis of Reliance Industries’ liquidity ratios for FY23 shows that the current Ratio stood at 1.07. This suggests that the company can technically cover its short-term liabilities with its current assets. However, the Ratio is just barely above the threshold of 1.0, which is generally considered safe for most industries. This indicates a need for Reliance to continue monitoring and potentially improving its short-term debt management.
While 0.9 is below average in one industry, 0.7 could be catastrophic in another. However, any ratio persistently below 1.0 merits concern for stock investors. It demonstrates the company’s inability to operate efficiently and convert assets into cash flow. The liquidity ratio also treats all liquid assets as equal, regardless of asset quality.
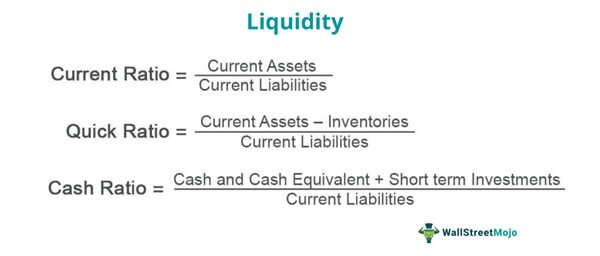
As a useful financial metric, the liquidity ratio helps to understand the financial position of a company. Quick ratio or acid test ratio is another liquidity ratio that determines a company’s current available liquidity. The current ratio implies the financial capacity of a company to clear off its current reporting stockholder equity obligations by using its current assets. Cash Ratio computes the company’s liquid assets such as cash, tradable securities. However, money is the most liquid form of assets, this ratio tells us the speed and limit at which a company can repay its present dues by using readily available assets.
It is calculated by dividing the total current assets, minus inventories and prepaid expenses, by total current liabilities. The basic liquidity ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations with its most liquid assets. Cash equivalents are assets that are quickly converted into cash, such as Treasury bills and short-term certificates of deposit. A liquidity ratio is a financial metric that measures a company’s ability to pay off its short-term debts and obligations. The liquidity ratio evaluates the amount of liquid or current assets available to cover the company’s current liabilities that are due within one year.
Leave a Reply